ELECTRONICS, PHOTONICS, INSTRUMENTATION AND COMMUNICATIONS
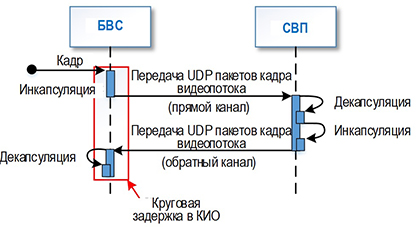
This research considers the dependence of the delay and loss of video stream frames compressed by neural network codec developed on the basis of neural network variation auto-encoder on the size of transmitted frames in the realization of information exchange channels between unmanned aviation system and external pilot station in the ground segment of hybrid orbital-terrestrial communication network taking into account the distance between them when using 3G and LTE data transmission technologies are used. The Relevance of the research is conditioned by the necessity to achieve a given level of service quality for FPV control of UAVs in communication networks. Methods used. In this research, the applied transmission delays and frame loss of FPV control video stream when using neural network codecs are measured by in-situ experiment. The applied delays and losses take into account segmentation, packet recovery and transmission of multiple UDP packets for each payload. Additionally, the Rosenblatt-Parzen method reconstructs the probability density distributions of delay probabilities. Results. Estimates of average values of transmission delay and frame loss of video stream (compressed by neural network codec) when using 3G and LTE data transmission technologies taking into account different distances between the unmanned system and the external pilot's station are obtained. The distributions of video stream delay dependencies on the payload size are reconstructed. The character of video stream delay distribution formed by neural network codec is found. The Novelty of the obtained results lies in the study of the nature of delays and frame losses of the FPV-control service video stream transmitted through mobile communication networks at the application layer of the OSI model when using neural network codecs. Practical significance. The results can be used in modeling of information exchange channels for FPV control in order to form the optimal configuration of the used neural network codecs.
Relevance. The use of multi-antenna technologies in the form of signal precoding is a basic condition for increasing spectral efficiency in modern mobile communication systems in combination with the transition to the millimeter wave frequency band. Propagation conditions in the millimeter wave require the use of antenna arrays in communication systems to compensate for propagation losses and directional transmission and reception of user signals. When transmitting multiple parallel spatial user data streams, signal precoding is used to implement spatial multiplexing and improve the spectral efficiency of the system. A hybrid architecture for constructing a multi-antenna system and precoding, consisting of analog and digital parts, is considered. But reducing the number of radio frequency paths leads to a decrease in the possibility of spatial multiplexing compared to a completely digital system. In this regard, it is important to select the optimal number of radio frequency paths to obtain maximum spatial multiplexing, taking into account the current conditions of signal propagation and spatial correlation of the communication channel.
The purpose of the study is to determine the effect on the spectral efficiency of the choice of the number of used radio frequency paths in a hybrid precoding system.
The research methods consist of simulation modeling of a hybrid precoding algorithm. To solve the problem of numerical modeling of hybrid precoding, implementations of a MIMO channel of millimeter waves are used, obtained using the open channel model software package QuaDRiGa.
The results are presented in the form of distribution functions of the spectral efficiency of the hybrid precoding system, obtained on the basis of channel implementations in a certain propagation scenario.
The novelty lies in the numerical determination of the channel parameters of a multi-antenna communication system in the millimeter range and the use of the distribution of eigenvalues of the obtained channel implementations to study the influence of the number of radio frequency paths on the spectral efficiency of a communication system with hybrid precoding achievable under given conditions.
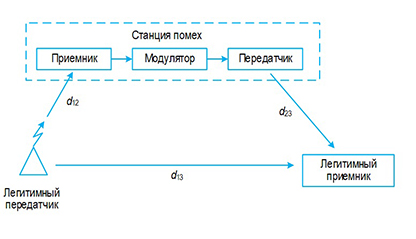
Presently, it is very important to design wireless systems that are resistant to jamming by adversary. It is well known technology to execute so called spread spectrum signals in order to prevent such attacks, especially under the conditions when enemy is superior i1n power against legitimate users. Moreover, adversary is able to estimate legitime signal parameter (type of modulation, duration of intervals ctr) However, such approach be vulnerable in the case of the use by adversary so called retransmitted interferences.
The purpose of this article is to increase the efficiency of spread spectrum signals transmission under the action of retransmitted interference, the power of which exceeds the power of the legitimate signals.
The essence of the proposed solution is to use spread spectrum phase-frequency modulated signals for information transmission, generated using independent unpredictable pseudorandom sequences that are different at the transmitted and non-transmitted frequencies. Instant phases are randomized independently for bit intervals at the transmitting side. Theoretically, using appropriated mathematical technique, the formula is derived for calculating of the bit error probability for the proposed system with different choice of its parameters. It is proved that for correctly selected parameters, the probabilities of bit errors are approaching to such values that occurs qcceptable to use next error correcting codes, which will ensure reliable delivery of important information.
The scientific novelty of our method consists in the use an unpredictable pseudorandom sequence at a frequency that is not currently being transmitted, in a randomized phase shift at each bit interval when forming a broadband signal, as well as in optimizing the parameters for the proposed radio communication system, that improved significantly further use of error-correcting code.
The theoretical significance consists in the correct proof of the formula for the bit error probabilities and further estimation the conditions for application of error correction codes.
The practical significance lies in design of interference proof wireless communication system that after some further elaboration of synchronization system and error correction codes, can be applied in practice under very hard interference environment.
At present, passive digital frequency synthesis systems are increasingly used in exciters of radio transmitting devices and in heterodynes of radio receiving devices of radar, radio navigation and radio communication systems. Such systems are based on a finite state machine - a device or program that can change its states at discrete moments of time, integer multiples of the clock interval, have a finite number of stable states, i.e. have a finite memory. Therefore, the problem of analytical description of the states of such machines at any predetermined moment of time is relevant.
The purpose of this work is to compactly describe the transition functions and output functions of machines used in passive digital frequency synthesis systems. An essential feature of the analysis and design of such machines is the requirement to minimize the level of functional phase-pulse modulation of the output pulse flow, i.e. minimization of the time error between the flow of generated pulses and the ideally uniform (hypothetical) flow of pulses of the required frequency. A quasi-periodic pulse sequence with a minimum time deviation from the hypothetical sequence is called a quasi-uniform pulse sequence. In addition, the purpose of this work is to correctly prove the optimality of a quasi-uniform sequence from the point of view of the minimum functional phase-pulse modulation of the output pulse flow.
The research methods are based on the use of number-theoretical transformations of the main parameter of the machine - its division coefficient N = P / Q, where P and Q, respectively, are the number of clock and output pulses in the period of non-uniformity of the output flow of the quasi-uniform sequence.
Result. New analytical expressions for describing the states of the machine at any predetermined moment of time, expressions for the instantaneous (current) phase of the machine and the instantaneous (current) frequency of the quasi-uniform pulse sequence at its output are obtained. Such expressions are convenient for analyzing and calculating machines used in passive digital frequency synthesis systems.
The theoretical significance lies in the development of a method for describing the states of an optimal finite state machine in the time domain and obtaining the corresponding analytical expressions.
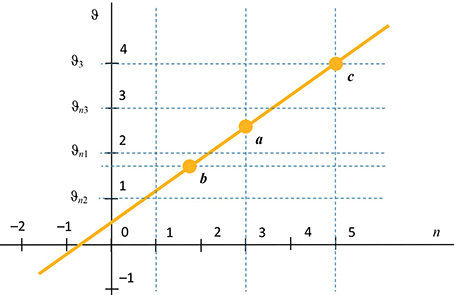
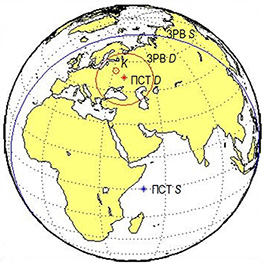
Relevance. The existing methods of coordinate measurement, such as goniometric, goniometric-range-measuring, difference-range-measuring, total-range-measuring are well studied and optimized. However, the application of these methods is not always possible or advisable, which stimulates the development and study of new methods and their integration with the existing ones. The article presents the developed method of coordinate measurement of the earth station, based on the use of two spacecraft. The derivation of analytical relationships for calculating the coordinates of earth stations based on the values of mutual time delays and frequency shifts is shown. The specified time delays and frequency shifts are due to different distances and Doppler frequency shifts of the same implementations of radio signals on different radio paths.
The main expressions for time delays and frequency shifts of radio signals of earth stations retransmitted by spacecraft are presented. A system of three independent equations is composed. The first equation is the difference-range equation, the second is the difference-radial-velocity equation, and the third is the equation of the Earth's reference ellipsoid. The result of solving the system of equations is the coordinates of the earth station.
The study used the methods of modeling and mathematical analysis. When solving the second-order equation, the iterative Newton-Raphson method was used with the expansion of functions in Taylor series with an accuracy of up to the first derivatives.
A particular example of calculation is given as an illustration of the developed method. The developed method of coordinate measurement is invariant to the type of orbits of spacecraft used to determine the coordinates of earth stations. Two spacecraft are given as an example: the first is in geostationary orbit, the second is in low orbit.
The scientific novelty of the developed technical solution is the unambiguous one-time determination of the coordinates of earth stations located on the surface of the Earth's reference ellipsoid, based on the use of only two spacecraft. In this case, there is no need for synchronization with the radiation of radio signals of earth stations, which is a necessary condition for most existing methods of coordinate measurement.
The practical significance of the proposed combined (difference-range and difference-Doppler) method of coordinate measurement of earth stations lies in the possibility of its application in existing and prospective radio monitoring complexes for assessing the coordinates of earth stations that illegally use the frequency-time resource of a spacecraft, as well as being sources of intentional or unintentional radio interference.
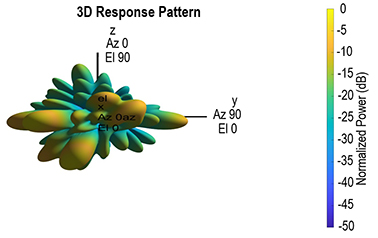
Relevance. The active use of wireless technologies requires the development of controls for wireless networks, in particular Wi-Fi networks. Radio monitoring services solve the tasks of detecting, identifying and localizing unauthorized access points and clients. An effective tool for bearing radio signals is correlation interferometric direction finders based on two-channel receiving equipment and a multi-element antenna system. The development of methods of joint identification and bearing makes it possible to separate the bearings of a large number of signal sources operating in the same frequency range with time division. In this work, the emphasis is placed on the detection of target signals and the identification of source features from them. The indicators of the quality of bearing will also significantly depend on the success of these operations.
The aim of the work is to investigate the possibilities of increasing the interference resistance of detecting and identifying Wi-Fi signals through the combined use of two channels of a correlation interferometric detector.
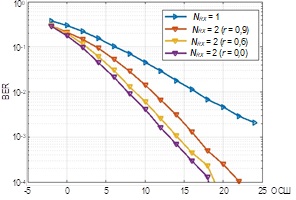
Methods. The paper uses statistical computer modeling methods that take into account the presence of fading due to multipath propagation channel and the correlation of radio signals caused by the proximity of receiving antennas.
Decision. Algorithms of detection, time-frequency synchronization and demodulation of Wi-Fi signals are considered. Methods of combining receiving channels in signal processing are proposed. The noise immunity of the proposed two-channel signal processing algorithms in the presence of quasi-stationary Relay fades and correlation of receiving channels is investigated.
Novelty. Algorithms for two-channel detection, time-frequency synchronization and demodulation of Wi-Fi signals have been developed.
Practical significance. The combined use of two reception channels for the detection and identification of Wi-Fi signals allows you to increase the reliability of radio monitoring systems by 4‒7 dB, even if there is a correlation between the channels.
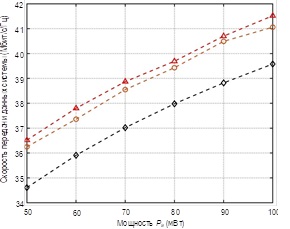
In remote areas and disaster-stricken regions, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can serve as base stations, providing wireless communication to ground users. Due to their high mobility, low cost, and rapid deployment and retrieval capabilities, UAVs can continuously adjust their position in three-dimensional (3D) space, improving wireless connectivity and enhancing data transmission rates. In this paper, we investigate the problem of ABS (Aerial Base Station) deployment in 3D space and power allocation with the aim of maximizing the data transmission rate in the system. To address this non-convex problem, we propose Q-learning, a reinforcement learning algorithm. By using the ABS as an agent, the algorithm enables the ABS to explore the state space and take actions based on an ϵ-greedy policy (optimal epsilon value) to determine its 3D position and power allocation. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms individual position optimization and power allocation optimization.
The purpose of this article is to study the efficiency of using modern artificial intelligence methods to optimize the use of resources of airborne base stations of public communication networks.
The essence of the proposed solution is to use modern artificial intelligence methods, namely: the Q-learning method and the epsilon-greedy ϵ-greedy algorithm to ensure joint optimization of the placement of airborne base stations and power distribution to maximize the data transfer rate. The system has an implementation in the form of a simulation program. Simulation experiments have shown that the use of the Q-learning reinforcement learning method and the epsilon-greedy e-greedy algorithm for joint optimization provides a higher overall data transfer rate in the system compared to optimizing only the location or power distribution.
The scientific novelty of the proposed solution is that joint optimization of the placement of an airborne base station and power distribution made it possible, in contrast to known results, to establish that the flight altitude of a UAV with a base station installed on it when optimizing only the location will be higher than the flight altitude of a UAV when jointly optimizing the location and power distribution.
The practical significance is the possibility of developing a methodology for planning public communication networks using airborne base stations to obtain a higher overall data transfer rate on the corresponding network fragment.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES AND TELECOMMUNICATION
The relevance of the research is explained by the existing contradiction of the subject area, which consists in the communication infrastructure of the critical information infrastructure (CII) object dynamically changing in the process of functioning, as well as the methods of the intruder's impact on the CII object, as well as the methods of the intruder's impact on the CII object, which create preconditions for reducing the level of information security and the capabilities of the existing methods of assessing the object's security based on signatures, expert approach, as well as methods and means of ensuring information security, which do not allow taking into account such dynamics of changes in the level of information security of the object.
Purpose of the research. Provision of information security of communication infrastructure of CII objects by taking into account communication and configuration parameters, dynamics of interacting subjects.
Research methods. Mathematical methods of systems theory and system analysis of probability theory, methods of graph theory, methods of simulation modeling.
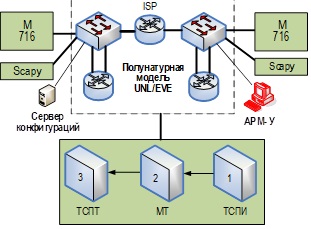
Results. The article presents a method of modeling of communication infrastructure that allows to form parametric accurate simulation models of the CII object to study the properties of security and stability, to simulate the impact of an intruder on the CII object.
Novelty. A method of modeling the communication infrastructure based on configuration and communication parameters of the CII object has been developed, taking into account the dynamics of communication infrastructure interaction, its information security policy and intruder actions.
Theoretical significance. Development of information security methods in the field of modeling the communication infrastructure of CII objects on the basis of hypergraphs, nested colored Petri nets, allowing to take into account the dynamics of interacting subjects (communication and configuration infrastructure, information security policy, the impact of the intruder).
Practical significance. The modeling method allows to take into account configuration and communication peculiarities of construction and functioning of the CII object, parameters of the intruder's impact on the CII object, the existing security policy, to model the stability property, to conduct research of the influence of interacting subjects on the security of the CII object, to reduce the dependence on expert assessments, to receive parametrically justified assessments of the security of the communication infrastructure of the CII object.
The relevance of the topic is justified by the software reverse engineering methodology lack required to resolve the following scientific contradiction in the field (as a contrast between need and opportunity): on the one hand, vulnerability search is most effective in those program representations in which they were implemented (e.g. source code, algorithms or architecture); on the other hand, as a rule, only machine code is available for analysis, which is poorly suited for identifying high-level vulnerabilities (i.e. from earlier representations). The main author's study, the final stage of which is given in the article, is devoted to the creation of the this methodology elements (concept, model, method, algorithms, metrics, as well as their implementations).
The purpose of this article is to discuss 25 problematic issues (the so-called scientific discussion) that arose in the main study devoted to the software reverse engineering development based on genetic algorithms. The main application of the research results is both obtaining a program representation suitable for expert (and other) analysis for vulnerabilities, and their direct search using the built-in signature method. At the same time, resolving even a part of the issues will significantly increase the efficiency of such genetic reverse engineering.
The following methods were used in the work: the main research results analysis to identify problematic issues, ways to resolve them synthesis, as well as issues systematization and scoring from the standpoint of ways to eliminate them for an overall assessment of the scientific work completeness.
A causes of each issue detailed research allowed us to determine ways to resolve them, the feasibility of which also justifies the main research results. In particular, problematic issues are based both on some absence of theoretical tools necessary for genetic reverse engineering, and on the insufficient practical efficiency of others.
The scientific novelty of the issues lies in the fact that almost each of them is voiced for the first time.
The theoretical significance lies in the fact that the development of each problematic issue can both open a separate scientific study (or even a direction), and obtain new significant results.
The practical significance lies in the possibility of creating software solutions to resolve identified issues, which can also be applied to related tasks.
The article relevance is due to the growing threats to computer security of critical information resources, including in the education system, cyberattacks types and trends diversity, requiring known analysis and forecasting methods differentiation, including those based on the use of time series theory. The article aim is to study the possibilities and limitations of using time series theory methods to analyses and predict the cyber attacks dynamics on the departmental university example that trains specialists in many security types: technosphere, fire, information and other. Hypothesis about the influence of the initial data nature on the methods for cyberattacks number time series analyzing and forecasting choice, and primacy of initial data on the solving these tasks effectiveness was stated and tested. Analyses of the corporate information system firewall monitoring logs are performed. On their basis, time series number of different types of attacks are constructed. The tasks of building mathematical models and current forecasting have been solved. An integrated approach to their solution based on preliminary processing, testing of statistical hypotheses about DS- and TS-stationarity and use of different forecasting methods was applied. The obtained results novelty is due to known methods of time series forecasting theory application to studying the dynamics of cyberattacks on the departmental university corporate information system. Theoretical significance consists in establishing the limits of their application possibility due to the studied time series variability, as well as in confirming the initial data primary quality over the existing methods and models. The practical value is determined by the time series models construction that allow solving tasks of cyberattacks number current forecasting.
ISSN 2712-8830 (Online)