ELECTRONICS, PHOTONICS, INSTRUMENTATION AND COMMUNICATIONS
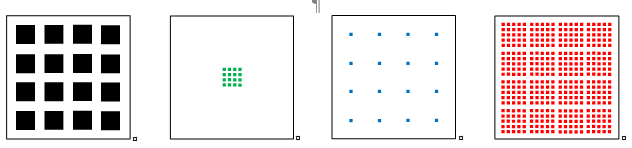
Relevance. Holography is becoming one of the most promising areas of visualization of three-dimensional objects, which justifies the emergence of a certain scientific interest in this area of research. There is a general global trend of intensifying the work of specialists on the problem of using holographic technologies in various areas of human activity. Trends in the implementation of holographic services and holographic communication today already require a revision of the principles of planning, designing and building existing communication networks, as well as approaches to the implementation of sixth-generation networks 6G, which are based on the integration of various technologies and communication networks into a single network. A separate issue is the assessment of the quality of service and the quality of perception of holographic services by both objective and subjective assessment methods. There are practically no criteria for assessing the quality of a holographic image, including scales and methods for subjective assessment of the quality of holographic services. Moreover, the properties of the holographic flow are poorly understood, and even less so its influence on communication networks and requirements for network parameters, which makes the tasks of studying traffic characteristics and assessing the quality of service of holographic services very relevant.
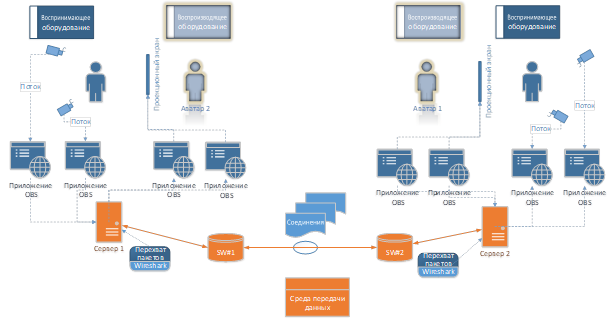
The aim of the work is to evaluate the quality of perception of holographic conference calls using a subjective evaluation method on a model network. The work uses methods of subjective assessment of the quality of perception. The materials presented in the article reflect the results of the authors' experimental research work on studying the problem of the quality of perception of holographic copies. A description of the developed scheme of a full-scale experiment is given.
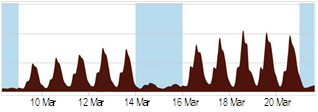
Results. The data obtained as a result of the work of an expert group on assessing the quality of perception are presented. The subjective assessment of the quality of perception of a holographic image begins to deteriorate with 8 connections and becomes unsatisfactory with 12 connections, which must be taken into account when planning experimental studies of work on assessing the quality of perception.
Novelty. For the first time, an assessment of the quality of perception of the provision of a holographic conferencing service was carried out using a subjective assessment method.
Theoretical significance. The influence of increasing the number of holographic traffic flows on the quality of perception of the received content is analyzed.
Practical significance. Expanding the possibilities for assessing the degree of user satisfaction with holographic services.
Relevance. The active transition to a massive digital infrastructure based on Internet of Things (IoT) technology has brought telecommunications networks to the level of dominant information resources. The one-time increase in the number of existing Internet services is inextricably linked to the growing variety of network anomalies on telecommunications equipment. In turn, existing methods of detecting network threats do not allow timely assessment of network traffic, which is characterized by a large number of parameters, and the detected anomalies from external interference do not have pronounced patterns.
The purpose of the study is to increase the efficiency of detecting traffic anomalies based on the results of processing its frame wavelet transform. The scientific task is to develop scientific and methodological approaches that allow effective analysis and timely detection of anomalies in network traffic. A comparative review of search methods for detecting network traffic anomalies, algorithms for detecting uncontrolled anomalies, traffic analysis methods based on local emission factor, binary trees, optical emission spectroscopy.
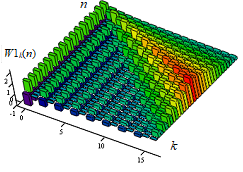
Decision. The results of the study of the possibility of detecting anomalies in the bitstream traffic based on the results of its multiple-variable transformation in the Haar wavelet basis are considered. The choice for further processing of the coefficients of the traffic decomposition matrix along the time shift variable is justified. It is proved that multiple-scale transformations not only increase the structural differences in traffic, but also open up the possibility of localization of anomalies that caused these differences.
The scientific novelty of the work is determined by the author's approach to detecting network traffic anomalies during the transition from the direct representation of a signal in the form of its discrete samples to coefficients formed from the matrices of its wavelet transformations, and, as a result, increasing its contrast with other signals with a similar structure.
Theoretical significance. The necessity and sufficiency of using wavelet coefficients instead of time samples of signals in the basis of the parent wavelet from the matrix of the generated frame is proved. The relationship between the Hurst indicators and the coefficients of the cross-correlation functions has been established.
Practical significance. The results obtained in the work, in the future, can be used in the construction of models for evaluating network traffic in conditions of deliberate, as well as methods for searching and synthesizing effective methods of protection against them.
Relevance. Provision of reliable and uninterrupted radio communication is critically important under changing climatic conditions of its operation. The combined effect of temperature and humidity can lead to changes in the electrical characteristics of transceiving devices and thereby disrupt the communication channel. In difficult climatic conditions of operation, due to constant temperature changes on the surface of the printed circuit boards, which are part of them, condensation can form, affecting the performance of the entire device. In this regard, the electrical characteristics change, which must be taken into account when designing critical REE. When designing transmission lines on printed circuit boards, it is reasonable to evaluate climatic impacts on it in a wide frequency range, which requires the development of new models and methods that allow taking into account these impacts.
Goal of the work: to evaluate the influence of the temperature of a thin film of water on the surface of a microstrip transmission line on its frequency dependences of S-parameters. Finite element methods and laboratory experiment were used.
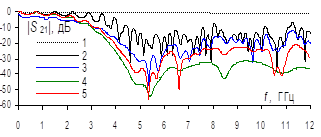
Results. A methodology to account for the effects of ambient temperature and humidity on the electrical characteristics of a microstrip transmission line (MTL) is presented, which allows evaluating the variation of the S-parameters of the line over wide ranges of frequencies, air temperature and humidity, as well as the chemical composition of the environment. The S-parameters of water in a container placed inside a coaxial chamber are measured over the frequency and temperature ranges of 10 MHz to 12 GHz and minus 50 to 100℃, respectively. Using the presented model, the frequency dependences of the electrical conductivity of water at different temperatures are calculated. It is shown that at positive temperature, the electrical conductivity can reach 6.5 Sm/m and at negative temperature it can reach 1.3 Sm/m. Using the developed methodology, the influence of different water electrical conductivity on the S-parameters of MTLs is evaluated. The influence of water and ice layer thickness on the S-parameters of MTLs was shown. It is found that models describing the electrical conductivity of water have an excellent influence on the electrical parameters of the transmission line. Novelty. A method of accounting for the influence of ambient temperature and humidity on the S-parameters of the transmission line is presented, which is characterized by the use of a model of water conductivity based on insertion losses calculated from the measured S-parameters of a coaxial chamber with water in the container when its temperature is changed.
Practical significance: a model and a methodology for taking into account the impact of temperature and humidity of the environment on the MTL characteristics are presented, allowing estimating the S-parameters of the line in a wide range of frequencies, air temperature and humidity, as well as the chemical composition of the environment.
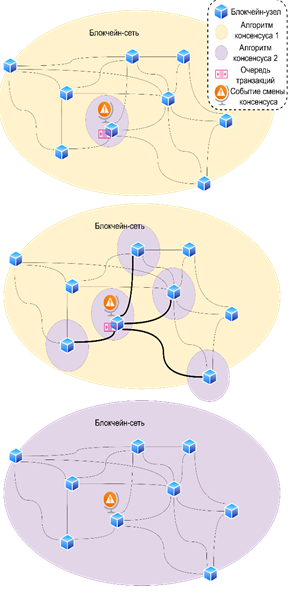
The relevance of the approaches and solutions proposed in the work is due to the desire for distributed computing and decentralization of system modules using blockchain technology in order to increase the autonomy, security and independence of system components. The implementation of blockchain technology for decentralization is hampered by the lack of flexibility in terms of the algorithm for making a single decision in the asynchronous system ‒ consensus, which affects the amount of generated network traffic and the requirements for the hardware component. Due to the changing nature of the transmitted traffic, the load on the communication channel, the time of day of traffic transmission, the equipment, and the network protocols used, the development of a single universal consensus algorithm is not possible, since it depends on a very wide range of variable and specific parameters characteristic of different tasks. The introduction of adaptation mechanisms to current network conditions and a change in the consensus algorithm without losing information and with a satisfactory level of delays would provide sufficient flexibility for further implementation in existing telecommunication systems. The purpose of this paper is to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed adaptive algorithm for choosing a consensus for blockchain networks.
The essence of the presented algorithm is to change the consensus algorithm on a section of the blockchain network upon reaching certain network conditions, which allows regulating the amount of generated load on the communication network to reduce the loss of transaction blocks and the subsequent delay in their processing. The proposed efficiency assessment model is based on mathematical modeling methods, differential equation analysis, queueing theory and network graphs. The analysis of the results showed the efficiency of the proposed model when comparing the results of the analytical calculation and the experiment. The scientific novelty of the proposed approach is to developing an adaptive consensus selection algorithm, as opposed to developing a universal consensus algorithm, and the efficiency assessment model of the proposed algorithm on the communication network, taking into account a number of parameters characterizing the devices and the section of the communication network.
The theoretical significance is in the universality of the proposed efficiency assessment model for calculating the synchronization speed of all nodes of the blockchain network with specified network parameters.
The practical significance of the proposed algorithm and efficiency assessment method lies in the formation of new approaches and opportunities for integrating blockchain technology into modern communication networks, abstracting from the problem of consensus selection in changing conditions of the communication network section.
Relevance. Management of the use of the radio frequency spectrum requires taking into account the actual occupancy of radio channels and frequency bands. However, the patterns of occupancy change underlying the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-R) Radiocommunication Sector documents do not fully meet the needs of practice. Some of the ITU-R recommendations are focused on estimating local occupancy for short time intervals; other recommendations involve measurements in stationary radio channels, although only a small part of real radio channels can be counted on to have the constant occupancy throughout the time axis. At the same time, the activities of many organizations, and therefore the resources they use, are subject to a daily cycle of activity, which allows us to recommend for consideration a model of occupancy change in accordance with the daily cycle.
The aim of the work is to develop a methodology for collecting information and forming an estimate of the daily occupancy change for the analyzed radio channels.
Methods used. The development of recommendations for the collection of data for occupancy monitoring is based on the practical approaches of radio monitoring services and classical methods of statistical analysis.
Novelty. In this paper, a new model for changing the occupancy of radio frequency channels in accordance with the daily cycle is proposed for use, as well as a statistically justified method for measuring occupancy.
Result. The proposed methodology allows us to obtain a practically oriented assessment of occupancy changes, which does not require replacing the fleet of equipment traditionally used by radio monitoring services; the necessary changes can be implemented with relatively simple software modification. The paper provides preliminary recommendations for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of measurements, based on a traditionally used mathematical apparatus, which involves limiting the relative measurement error. This entails the need for very long measurements for the most important low-occupied radio channels. So, it is necessary to look for alternative measurement accuracy requirements that would meet the real needs of radio monitoring services.
Practical significance. The acceptance of the developed methodology will eliminate the currently existing contradiction between the theoretical provisions underlying the ITU recommendations and the practice of conducting radio-controlled measurements.
Relevance. This work is the second part of a series devoted to the study of a set of positioning models in sixth-generation terahertz networks and solves the problems of systematizing algorithms and assessing the accuracy of determining the location of a user device depending on the configuration and size of the antenna array at the base station.
Purpose. Within the framework of the scientific problem of searching for means of achieving decimeter accuracy of coordinate estimates, outlined in the first part of the cycle, the analysis of accuracy assessment models, a review of algorithms and ways of their optimization, as well as a numerical experiment, performed in this study serve the purpose of justifying the configuration and dimensions of the antenna array used at the base station.
The research method is an analytical review of the state of the problem based on current scientific publications, conceptual modeling, categorical approach, expert combination, comparative analysis, formalization, mathematical and simulation modeling.
Solution / results. The paper presents models for assessing the accuracy of positioning in 6G terahertz networks, formalizes the relationship between primary measurements and coordinate estimates for multi-position and single-position positioning in the near and far zones. It provides an overview of algorithms for geometric positioning and positioning with training for cases of one-stage and two-stage processing; analyzes the specifics of implementing algorithms for simultaneous tracking and map construction. It provides an analysis of the features of optimizing algorithms in offline and online modes. Simulation modeling is used to assess the accuracy for a scenario of territorial distribution with direct visibility and ideal synchronization.
Novelty. Using simulation modeling tools, the achievement of decimeter accuracy of coordinate and orientation estimates of 1° in the terahertz range for a far-field model using a 1 GHz band and a composite antenna array of more than half a thousand elements has been scientifically substantiated.
The theoretical significance lies in establishing the dependence of the accuracy of coordinate and orientation estimates of the device on the configuration and dimensions of the antenna array at the base station.
The practical significance of the developed simulation model lies in the numerical justification of the limits of device positioning accuracy in sixth-generation networks depending on the antenna array used at the base station for a given scenario.
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATICS
Relevance. In recent decades, metaheuristic optimization methods have become popular for solving complex problems that require searching for global extrema. Algorithms such as genetic algorithm (GA), ant colony optimization (ACO), particle swarm optimization (PSO), as well as more modern approaches such as cat pack optimization (CSO) and gray wolf pack optimization (GWO) demonstrate high efficiency, but their application is often limited by the conditions of continuity and differentiability of the objective functions. This is a challenge when solving problems with discrete data, where such requirements are not met. In this context, the search for methods that allow adapting metaheuristic algorithms to work with discrete functions is of particular relevance.
Aim. The study is aimed at testing the hypothesis about the possibility of using a neural network trained on a limited set of discrete data as an approximation of a function sufficient for the correct execution of the GWO algorithm when searching for a global minimum. The implementation of this hypothesis can significantly expand the scope of GWO, making it available for a wider range of problems where functions are defined on discrete sets.
Methods. The study is based on the analysis of existing approaches and experimental verification of the hypothesis on two test functions: a linear function and a Booth function, which are widely used as standards for evaluating the performance of optimization algorithms. Numerical experiments were conducted using neural networks as an approximating model to obtain the results.
Solution. During the experiments, an analysis of the applicability of neural networks for approximating discrete functions was carried out, which showed the success of this approach. It was found that neural networks can approximate discrete functions with high accuracy, creating conditions for a successful search for a global minimum using the GWO algorithm.
Novelty. For the first time, a hypothesis was proposed and tested on the use of neural networks for approximating objective functions in metaheuristic optimization problems on discrete data. This direction has not previously received due coverage in the scientific literature, which adds significance to the obtained results and confirms the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Practical significance. The results of the study open up new prospects for the application of algorithms such as GWO in optimization problems based on discrete data, expanding the capabilities of metaheuristic methods and facilitating their implementation in a wider class of applied problems, including problems where the use of other methods is limited.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES AND TELECOMMUNICATION
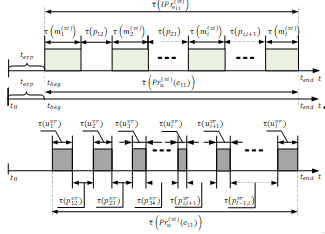
The relevance of the article is due to the need to protect information at all stages of creating an information system in the absence of appropriate organizational and technical support. To justify this kind of provision, mathematical models are needed that take into account the conditions and the random nature of the implementation of heterogeneous information processing processes in time at each stage, threats to its security and protection from these threats. The article discusses approaches to the development of such models based on the apparatus of flow theory and the theory of composite Petri ‒Markov networks, the possibilities of which for modeling the processes under study have not been previously considered.
The purpose of the article. To reveal the content of issues related to the justification of organizational and technical support for information protection at the stages of creating an information system, to show the need and ways to quantify threats to its security and protection from these threats. For this purpose, the methods of functional and structural analysis, probability theory and flow theory were applied. In the course of solving the scientific problem, the relevance of substantiating the organizational and technical support of information protection at the stages of creating information systems is shown, descriptive models of its processing processes are developed, time diagrams of threat scenarios are given in the absence of protection measures and in the conditions of using preventive organizational and technical measures, indicators and analytical ratios for their calculation are proposed. The scientific novelty of the article consists in the fact that for the first time it examines the issues of organizational and technical support for information protection at the stages of creating an information system, examines the theoretical aspects of quantifying threats to its security and protection from these threats based on flow theory and prospects for applying the theory of composite Petri-Markov networks. Significance (theoretical). The conditions for the implementation of the studied processes and the possibility of applying the theory of flows and the apparatus of composite Petri–Markov networks for their modeling are established. Significance (practical). The results obtained in the work can be used to justify the organizational and technical provision of information protection at the stages of creating information systems of various organizations (both state and non-state), for which the implementation of threats at these stages may lead to damage to their activities.
Relevance. Autonomous navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is one of the key challenges in the modern aerospace industry. Specifically, for small UAVs, the task of autonomous navigation becomes even more complex due to limitations in computational resources and sensor capabilities. Optimizing navigation methods under such conditions is a pressing issue that requires solutions capable of providing high performance with minimal resource consumption.
Objective. Improving the efficiency of autonomous navigation for small UAVs by using correlation methods for image comparison. Achieving this objective is linked to the development and evaluation of algorithms that provide high-speed and accurate navigation with limited computational resources. The work uses methods such as the autocorrelation function, Pearson correlation, the structural similarity index, and a simple neural network for image comparison.
Solution. The research showed that the autocorrelation-based approach demonstrates the best performance under low computational resources. It ensures high-speed processing of the entire image and shows optimal detection accuracy. Compared to other methods presented in the study, the autocorrelation approach is capable of working not only with noise in the "reference" map but also of using alternative areas with altered patterns as detected regions.
The scientific novelty of the study is determined by the systematic comparison of various methods applied to the task of image comparison for small UAVs with limited computational resources. Unlike well-known works in the field of correlation-extreme systems, this research focuses on the use of a "reference map" and a search area, representing two different images of the same terrain taken from different sources. This is a key difference, as most methods are not highly efficient in processing such images where patterns may differ significantly.
The practical significance of the developed algorithm lies in the fact that the proposed autocorrelation-based method can be used by developers of autonomous small UAV control systems to reduce computational load and increase data processing speed.
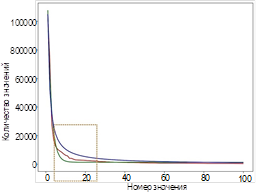
Currently, software engineering plays a key role in software development, one of the criteria for the development of which is the investigation of its factology and various scientific and practical patterns. An important aspect of this area is the logic of program execution, operating with internal data, and, in particular, constant values, the identification of patterns in which actualizes this research. The main applications of this pattern include obtaining fundamental knowledge about algorithms, creating new and expanding existing metrics for evaluating and comparing program code, developing methods for its optimization, using it in genetic programming, etc.
The purpose of this article is to obtain the frequency distribution of constant values in the source code of programs in the C programming language.
The essence of the presented approach is to create a method for statistical analysis of the text of the source codes of programs contained in the ExeBench dataset (which consists of a huge amount of source code of functions in the C programming language, their assembler code for various processor architectures, compilation errors and other information).
The proposed method is based on the use of algorithms for lexical and syntactic analysis of source code functions, semantic definition of constant types, and conversion of the recording of programming language symbols into the corresponding numeric or string values.
The method has an implementation in the form of a software tool in the Python programming language, given in the form of an intuitive pseudocode. Experiments using this prototype allowed us to obtain the desired distribution of constant values for the source code of programs in the C programming language. Analysis of the obtained results allowed us to make a number of important theoretical and practical conclusions regarding the most frequently used constants, the correspondence of the obtained distribution to the Zipf law and its proximity to the exponential function, the anomalous appearance of a number of constants in the Top 50, etc.
The scientific novelty of the proposed approach lies in the fact that the distribution of constant values for the source code of programs in the C programming language is obtained for the first time.
The theoretical significance consists in obtaining new fundamental knowledge regarding the features and patterns of source code constructions, which can be extended to other programming languages.
The practical significance consists in applying the distribution to a wide range of tasks, including the author's genetic reverse engineering, which in itself is a qualitatively new direction.
ISSN 2712-8830 (Online)