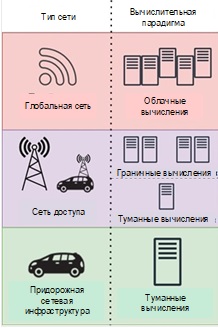
Analysis of Approaches to Optimization of V2X Systems: Clustering, Edge and Fog Computing
https://doi.org/10.31854/1813-324X-2024-10-3-7-22
EDN: TRWNON
Abstract
The review sets the task of analyzing existing solutions for communication systems based on Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technology using clustering and edge computing mechanisms in order to determine the conceptual model of the V2X system and the most significant indicators of quality of service (QoS), taking into account the application of the specified complex of technological solutions. The novelty of the work lies in the fact that the research is aimed at identifying the possibilities of integrating clustering mechanisms, edge and fog computing to determine optimal solutions for the deployment of roadside network infrastructure objects while maintaining high QoS indicators for communication equipment of this type. The result is that a scientifically based technological approach to constructing a conceptual model of a V2X system with specified QoS indicators has been proposed. Practical and theoretical relevance. The results obtained can be used in the design and deployment of V2X systems.
About the Authors
P. V. PlotnikovRussian Federation
A. G. Vladyko
Russian Federation
References
1. Mueck M., Karls I. Networking Vehicles to Everything: Evolving Automotive Solutions. Walter de Gruyter; 2018. 233 p.
2. Chen S, Hu J., Zhao L., Zhao R., Fang J., Shi Y., Xu H. Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X). Wireless Networks. Springer; 2023. 416 p.
3. Wang J., Shao Y., Ge Y., Yu R. A survey of vehicle to everything (V2X) testing. Sensors. 2019;19(2):334. DOI:10.3390/s19020334
4. V2X White Paper. Next Generation Mobile Networks Ltd.: San Jose; 2018.
5. Cooper C., Franklin D., Ros M., Safaei F., Abolhasan M. A Comparative Survey of VANET Clustering Techniques. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials. 2017;19(1):657–681. DOI:10.1109/COMST.2016.2611524
6. Bali R.S., Kumar N., Rodrigues J.J. Clustering in vehicular ad hoc networks: taxonomy, challenges and solutions. Vehicular Communications. 2014;1(3):134‒152. DOI:10.1016/j.vehcom.2014.05.004
7. Khan Z., Koubaa A., Fang S., Lee M.Y., Muhammad K. A Connectivity-Based Clustering Scheme for Intelligent Vehicles. Applied Sciences. 2021;11(5):2413. DOI:10.3390/app11052413
8. Abbas F., Liu G. Fan P., Khan Z. An efficient cluster based resource management scheme and its performance analysis for V2X networks. IEEE Access. 2020;8:87071–87082. DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992591
9. Jameel F., Javed M.A., Zeadally S., Jantti R. Efficient Mining Cluster Selection for Blockchain-Based Cellular V2X Com-munications. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2021;22(7):4064–4072. DOI:10.1109/TITS.2020.3006176
10. Abbas F., Fan P., Khan Z. A novel low-latency V2V resource allocation scheme based on cellular V2X communications. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2019;20(6):2185–2197. DOI:10.1109/TITS.2018.2865173
11. Paramonov A., Khayyat M., Chistova N., Muthanna A., Elgendy I.A., Koucheryavy A., et al. An Efficient Method for choosing Digital Cluster Size in Ultralow Latency Networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. 2021;2021:9188658. DOI:10.1155/2021/9188658
12. Luoto P., Bennis M., Pirinen P., Samarakoon S., Horneman K., Latvaaho M. Vehicle clustering for improving enhanced LTE-V2X network performance. Proceedings of the European Conference on Networks and Communications, EuCNC, 12‒15 June 2017, Oulu, Finland. IEEE; 2017. DOI:10.1109/EuCNC.2017.7980735
13. AlNagar Y., Hosny S., El-Sherif A.A. Proactive Caching for Vehicular Ad hoc Networks Using The City Model. Proceedings of the Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshop, WCNCW, 15‒18 April 2019, Marrakech, Morocco. IEEE; 2019. DOI:10.1109/WCNCW.2019.8902590
14. Plotnikov P., Vladyko A. Numerical Analysis of the Mathematical Model of a Cluster V2X-System. Proceedings of Telecommunication Universities. 2023;9(1):14–23. (in Russ.) DOI:10.31854/1813-324X-2023-9-1-14-23. EDN:JDPDSD
15. Plotnikov P.V., Tambovtsev G.I., Vladyko A.G. Software Module for Modeling the interaction of Edge Devices in VANET with one- and two-channel connectivity. Patent RF, no. 2023681939, 06.10. 2023. (in Russ.)
16. Liu L., Chen C., Pei Q., Maharjan S., Zhang Y. Vehicular edge computing and networking: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications. 2021;26:1145–1168. DOI:10.1007/s11036-020-01624-1
17. Fardad M., Muntean G.M., Tal I. A Blockchain-Enabled Vehicular Edge Computing Framework for Secure Performance-oriented V2X Service Delivery. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 2024. DOI:10.1109/TVT.2024.3394150
18. Fan W., Su Y., Liu J., Li S., Huang W., Wu F., Liu Y. Joint Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Vehicular Edge Computing Based on V2I and V2V Modes. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2023;24(4):4277–4292. DOI:10.1109/TITS.2022.3230430
19. Hou, P., Jiang, X., Lu, Z. et al. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation based on deep reinforcement learning in C-V2X edge computing. Applied Intelligence. 2023;53:22446–22466. DOI:10.1007/s10489-023-04637-x
20. Dai Y., Xu D., Maharjan S., Zhang Y., Joint Load Balancing and Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2019;6(3):4377–4387. DOI:10.1109/JIOT.2018.2876298
21. Guo H., Liu J., Ren J., Zhang Y. Intelligent Task Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2020;27(4):126–132. DOI:10.1109/MWC.001.1900489
22. Cai G., Fan B., Dong Y., Li T., Wu Y., Zhang Y. Task-Efficiency Oriented V2X Communications: Digital Twin Meets Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Wireless Communications. 2024;31(2):149–155. DOI:10.1109/MWC.012.2200465
23. Ye D., Yu R., Pan M., Han Z. Federated Learning in Vehicular Edge Computing: A Selective Model Aggregation Approach. IEEE Access. 2020;8:23920–23935. DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968399
24. Luo Q., Li C., Luan T.H., Shi W. Collaborative Data Scheduling for Vehicular Edge Computing via Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2020;7(10):9637–9650. DOI:10.1109/JIOT.2020.2983660
25. Vladyko A., Tambovtsev G., Podgornaya E., Chelloug S.A., Alkanhel R., Plotnikov P. Cluster-Based Vehicle-to-Everything Modelwith a Shared Cache. Mathematics. 2023;11(13):3017. DOI:10.3390/math11133017
26. Bonomi F. Connected vehicles, the internet of things, and fog computing. Proceedings of the Eighth ACM International Workshop on VehiculAr Inter-NETworking, VANET 2011, Las Vegas, USA, 23 September 2011. 2011.
27. Khattak H.A., Islam S.U., Din I.U., Guizani M. Integrating fog computing with VANETs: A consumer perspective. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine. 2019;3(1):19–25. DOI:10.1109/MCOMSTD.2019.1800050
28. Sarrigiannis I., Contreras L.M., Ramantas K., Antonopoulos A., Verikoukis C. Fog-Enabled Scalable C-V2X Architecture for Distributed 5G and Beyond Applications. IEEE Network. 2020;34(5):120–126. DOI:10.1109/MNET.111.2000476
29. Alvi A.N., Javed M.A., Hasanat M.H.A., Khan M.B., et al. Intelligent task offloading in fog computing based vehicular networks. Applied Sciences. 2022;12(9):4521. DOI:10.3390/app12094521
30. Tonguz O.K., Viriyasitavat W. Cars as roadside units: A self-organizing network solution. IEEE Communications Magazine. 2013;51(12):112‒120. DOI:10.1109/MCOM.2013.6685766
31. Karunathilake T., Forster A. A survey on mobile road side units in VANETs. Vehicles. 2022;4(2):482‒500. DOI:10.3390/vehicles4020029
32. Guerna A., Bitam S., Calafate C.T. Roadside unit deployment in internet of vehicles systems: A survey. Sensors. 2022;22(9):3190. DOI:10.3390/s22093190
33. Ercan S., Ayaida M., Messai N. How mobile RSUs can enhance communications in VANETs? // Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications, WINCOM, 16‒19 October 2018, Marrakesh, Morocco. IEEE; 2018. DOI:10.1109/WINCOM.2018.8629641
34. Lee J., Ahn S. Adaptive configuration of mobile roadside units for the cost-effective vehicular communication infrastructure. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. 2019;2019:6594084. DOI:10.1155/2019/6594084
35. Bitaghsir S.A., Kashipazha S., Dadlani A., Khonsari A. Social-aware mobile road side unit for content distribution in vehicular social networks. Proceedings of the Symposium on Computers and Communications, ISCC, 29 June 2019 ‒ 03 July 2019, Barcelona, Spain. IEEE; 2019. DOI:10.1109/ISCC47284.2019.8969669
36. Reis A.B., Sargento S., Tonguz O.K. Parked cars are excellent roadside units. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2017;18(9):2490–2502. DOI:10.1109/TITS.2017.2655498
37. Qin P., Fu Y., Feng X., Zhao X., Wang S., Zhou Z. Energy-efficient resource allocation for parked-cars-based cellular-V2V heterogeneous networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2022;9(4):3046‒3061. DOI:10.1109/JIOT.2021.3094903
38. Evariste T., Kasakula W., Rwigema J., Datta R. Optimal exploitation of on-street parked vehicles as roadside gateways for social IoV ‒ a case of Kigali City. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity. 2020;6(3):73. DOI:10.3390/joitmc6030073
39. Li G., Ma M., Liu C., Shu Y. Routing in taxi and public transport based heterogeneous vehicular networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference, TENCON, 22‒25 November 2016, Singapore, Singapore. IEEE; 2019. p.1863‒1866. DOI:10.1109/TENCON.2016.7848344
40. Jiang X., Du D.H.C. Bus-VANET: A bus vehicular network integrated with traffic infrastructure. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine. 2015;7(2):47‒57. DOI:10.1109/MITS.2015.2408137
41. Heo J., Kang B., Yang J.M., Paek J., Bahk S. Performance-cost tradeoff of using mobile roadside units for V2X communication. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 2019;68(9):9049‒9059. DOI:10.1109/TVT.2019.2925849
42. Kim D., Velasco Y., Wang W., Uma R.N., Hussain R., Lee S. A new comprehensive RSU installation strategy for cost-efficient VANET deployment. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 2016;66(5):4200–4211. DOI:10.1109/TVT.2016.2598253
43. Ni Y., Zhao C., Cai L. Hybrid RSU management in cybertwin-IoV for temporal and spatial service coverage. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 2022;71(5):4596‒4606. DOI:10.1109/TVT.2021.3138749
44. Plotnikov P.V., Tambovtsev G.I., Vladyko A.G. Performance Evaluation of V2X Model with a Mobile Road Side Units. Proceedings of the Intelligent Technologies and Electronic Devices in Vehicle and Road Transport Complex, TIRVED, 15‒17 No-vember 2023, Moscow, Russian Federation. IEEE; 2023. DOI:10.1109/TIRVED58506.2023.10332617
45. Plotnikov P.V., Tambovtsev G.I., Vladyko A.G. Numerical Analysis of roadside Units Deployment Models in V2X Communication System. Proceedings of the Systems of Signals Generating and Processing in the Field of on Board Communication, 12‒14 March 2024, Moscow, Russian Federation. IEEE; 2024. DOI:10.1109/IEEECONF60226.2024.10496720
Review
For citations:
Plotnikov P.V., Vladyko A.G. Analysis of Approaches to Optimization of V2X Systems: Clustering, Edge and Fog Computing. Proceedings of Telecommunication Universities. 2024;10(3):7-22. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.31854/1813-324X-2024-10-3-7-22. EDN: TRWNON


































